3 Needs for Seeds®
SEED GERMINATION
W.O.W. - Water. Oxygen. Warmth.®
Seed germination is the process by which a seed develops into a new plant. It begins when a seed absorbs water, triggering biochemical changes that activate growth. The seed's outer covering, called the seed coat, softens, allowing the embryo inside to break through. During germination, the root (radicle) or “taproot” emerges first, anchoring the plant when placed in the soil or preferred grow medium, followed by the shoot (plumule), which grows upward toward the light. Environmental factors like water, oxygen and temperature are essential for successful germination.

SOAKING SEEDS
Understanding the benefits of soaking your seeds for increased success when germinating seeds.
1. Softens the Seed Coat:
Many seeds have a hard outer shell or seed coat that can be tough for the sprout to break through. Soaking the seeds softens the coat, making it easier for the embryo inside to emerge and begin growing
2. Speeds Up Germination:
Soaking seeds helps to kickstart the germination process by allowing the seed to absorb water, which activates enzymes that break down stored nutrients. This reduces the time it takes for the seed to sprout, allowing for faster growth compared to dry seeds.
3. Promotes Even Water Absorption:
When seeds are soaked, they absorb water uniformly. This ensures that the entire seed is hydrated and ready to sprout, which can improve germination rates and result in more even growth for all seeds planted.
4. Helps to Break Dormancy:
Some seeds have natural dormancy mechanisms that prevent them from germinating until specific environmental conditions are met. Soaking can help break this dormancy.
5. Reduces the Risk of Disease:
Soaking seeds in a solution such as a mild fungicide or natural substance (like hydrogen peroxide) can help kill off harmful bacteria or fungi on the seed's surface. This can reduce the risk of diseases during the early stages of growth.
6. Improves Seed Viability:
By soaking seeds, you can also identify those that are not viable. Seeds that float to the top or don’t absorb water properly are usually not capable of germinating, allowing you to discard them before planting, and saving space and resources for the viable seeds.
Soaking seeds before germinating can lead to quicker, more successful germination, reduce the likelihood of disease, and help ensure that the seeds have the best possible start to their growth.

SEED GERMINATION
Ideal seed germination conditions are essential for ensuring the best chances of success for seed sprouting and early growth. These conditions include factors like moisture, oxygen, temperature and seed quality. Here’s a breakdown of the ideal conditions for seed germination:
1. Moisture:
Why it’s important: Seeds need water to initiate the biochemical processes that trigger germination. Moisture softens the seed coat, allowing the embryo to grow and expand.
Ideal conditions: Keep the environment consistently moist but not waterlogged. Too much water can cause the seeds to rot or "drown", while too little can hinder germination.
2. Oxygen:
Why it’s important: Seeds need oxygen for respiration to generate the energy required for growth during germination.
Ideal conditions: Ensure that you allow air to reach the seed. Avoid waterlogged conditions, which can limit oxygen flow to the seed.
3. Humidity:
Why it’s important: Humidity helps maintain moisture levels around the seeds and creates a favorable environment for sprouting.
Ideal conditions: Maintain a humid environment, especially in dry conditions. This will help prevent the seeds from drying out before germination is complete.
4. Temperature:
Why it’s important: Temperature influences the rate of enzymatic activity inside the seed. Most seeds have a specific temperature range at which they germinate best.
Ideal conditions: Temperatures can range anywhere between 65°F (18°C) and 90°F (32°C) for different varieties of seed. Varied seeds have diverse temperature needs, with some requiring cooler or warmer conditions. Research your seed's ideal requirements before starting germination.
5. Seed Quality:
Why it’s important: Healthy, viable seeds are more likely to germinate successfully. Poor-quality or old seeds may have reduced germination rates.
Ideal conditions: Use fresh seeds that are stored properly (in a cool, dry place). If you're unsure about the viability of old seeds, provide your seeds with ideal conditions and be patient.
6. Time:
Why it’s important: Seeds need time to go through the germination process and sprout. The time needed for germination depends on the quality, type of seed and the environmental conditions.
Ideal conditions: Be patient and avoid disturbing seeds during the germination process. Keep the environment consistent and monitor the progress.
Ensuring successful germination is a combination of seed quality, and the right balance of water, oxygen, and warmth. Providing these factors will give your seeds the best possible chance of sprouting and growing into healthy plants.
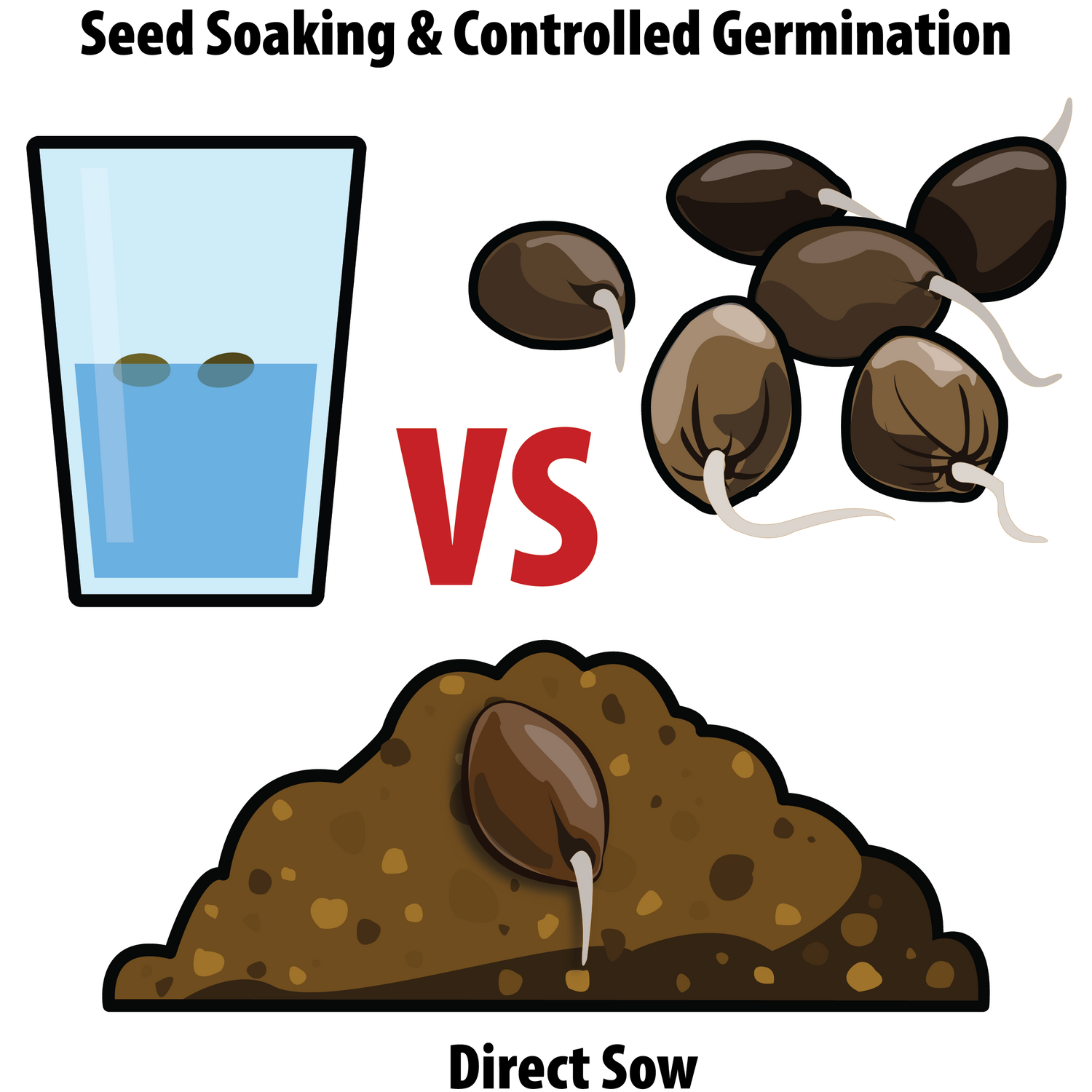

Advantages of Soaking Seeds and Germinating in a Controlled Environment
Soaking seeds and germinating them in a controlled environment, as opposed to direct sowing in the ground, offers several key advantages. Here are some of the benefits of each approach.
1. Faster Germination:
Seed that are soaked & germinated in a controlled environment like the Cannakan® systems often see faster and more consistent results. This is because the Cannakan® creates a convection ensuring your seeds receive constant moisture and warmth, which can stimulate quicker sprouting.
2. Higher Germination Rates:
Why it’s advantageous: In a controlled environment, seeds are more likely to germinate successfully because you can ensure that the temperature, moisture, and other conditions are ideal for growth. This approach also helps identify non-viable seeds, reducing the likelihood of wasting time, resources and space on seeds that won’t sprout.
3. Better Control Over Conditions:
A controlled environment (like the Cannakan® system) allows you to be in control of factors like temperature, humidity, and water levels with precision. This results in improved, more consistent and repeatable conditions for germination and early growth.
4. Better Visibility:
You can clearly see the seeds as they begin to sprout, allowing you to monitor the progress of each seed as well as identify any issues early on.
5. Prevents Seed Rot:
With the Cannakan® seeds are kept in a controlled moisture environment that eliminates the risk of overwatering, which can lead to seed rot, a common issue with direct sowing.
6. Space Efficiency:
Our method allows you to germinate many seeds in a small space before transplanting them, making it useful for maximizing space, especially indoors or in limited garden areas.
7. Identify Quality Traits:
You can select the seeds that germinate more successfully, ensuring that you don’t waste space by planting seeds that don't meet your specific requirements . This way, you only plant healthy, more viable seedlings.
Soaking and germinating in a controlled environment is ideal for gardeners looking for a head start, more control over conditions, and higher success rates.

Hydrogen peroxide and its benefits:
This section is only our opinion based on research & tests we have done.
Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) can be beneficial to seed germination for several reasons, helping to create optimal conditions for seeds to sprout and grow. Here are the key benefits of using hydrogen peroxide in seed germination:
1. Prevents Fungal and Bacterial Infections
Why it’s beneficial: Hydrogen peroxide inactivates microorganisms (bacteria, yeasts, fungi, viruses, and spores) through oxidization.
It helps reduce the risk of disease germination by acting as a disinfectant, killing bacteria, fungi, and other pathogens on seeds, thereby promoting healthier plant growth and reducing the likelihood of disease spreading during germination.
How it helps: Soaking seeds in a dilute solution of hydrogen peroxide (typically around 2-5%) can reduce the risk of infection, ensuring the seeds have a healthier environment to sprout.
2. Oxygen Release
Why it’s beneficial: Hydrogen peroxide breaks down into water (H₂O) and oxygen (O₂). The oxygen released by this breakdown of hydrogen peroxide helps improve the oxygen availability to the seeds.
How it helps: Seeds need oxygen for respiration during germination, and more oxygen can speed up the metabolic processes within the seed, promoting quicker and more uniform and successful germination.
3. Breaks Seed Dormancy
Why it’s beneficial: Some seeds have a natural dormancy mechanism that prevents them from germinating until certain conditions are met. Hydrogen peroxide can help break down these dormancy barriers in some seed types, allowing them to germinate more easily.
How it helps: For seeds with hard coats or those that are difficult to sprout, a hydrogen peroxide soak can soften the seed coat or activate dormant pathways, encouraging the seed to break dormancy and start germinating.
4. Promotes Stronger Root Growth
Why it’s beneficial: Hydrogen peroxide can help stimulate root development by providing additional oxygen to the germinating seed. Stronger, healthier roots can better anchor the seedling and absorb nutrients..
How it helps: The extra oxygen improves cellular respiration in the seed, boosting energy production for root growth, which is critical for establishing a healthy plant.
5. Helps with Seed Scarification
Why it’s beneficial: Some seeds have hard outer coatings that are resistant to water absorption, making germination difficult. Hydrogen peroxide can act as a mild scarifying agent, helping to break down these tough seed coats.
How it helps: By soaking seeds in hydrogen peroxide, you can soften or break down the seed coat more effectively, allowing water to penetrate and initiate germination.
6. Encourages Faster Germination
Why it’s beneficial: By promoting overall seed health, oxygen availability, and disease resistance, hydrogen peroxide can lead to faster sprouting compared to seeds that are not treated.
How it helps: Faster germination is beneficial for getting seedlings off to a strong start, especially when you're growing plants with short growing seasons or those that require quicker germination.
How to Use Hydrogen Peroxide for Seed Germination:
Important Consideration when Soaking and germinating seeds: Soak seeds in a diluted hydrogen peroxide solution (about 2-5% H₂O₂ and 95-98% water). This helps disinfect the seeds and promotes healthier germination

